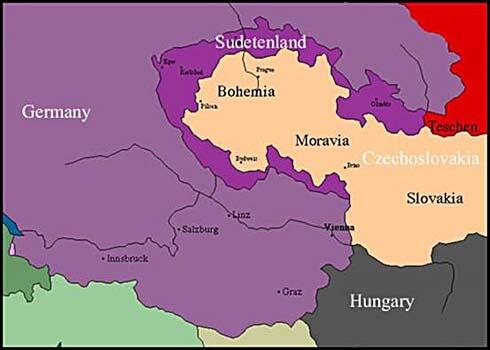
The Sudetenland
For over 1000 years the border region called Sudetenland between Bohemia and Germany was part of several legal Czech monarchies. Around 25% of the population were German. After the First World War the Sudetenland (some 11,000 square miles) became part of Czechoslovakia.
Until Adolf Hitler came to power most Sudeten Germans were content to remain in Czechoslovakia but in 1935 a Sudten-German Party, financed from within Nazi Germany, began to complain that the Czech-dominated government discriminated against them. German's who had lost their jobs in the depression began to argue that they might be better off under Hitler.
Adolf Hitler wanted to march into Czechoslovakia but his generals warned him that with its strong army and good mountain defences Czechoslovakia would be a difficult country to overcome. They also added that if Britain, France or the Soviet Union joined on the side of Czechoslovakia, Germany would probably be badly defeated. One group of senior generals even made plans to overthrow Hitler if he ignored their advice and declared war on Czechoslovakia.
In September 1938, Neville Chamberlain, the British prime minister, met Hitler at his home in Berchtesgaden. Hitler threatened to invade Czechoslovakia unless Britain supported Germany's plans to takeover the Sudetenland. After discussing the issue with the Edouard Daladier (France) and Eduard Benes (Czechoslovakia), Chamberlain informed Hitler that his proposals were unacceptable.
Adolf Hitler was in a difficult situation but he also knew that Britain and France were unwilling to go to war. He also thought it unlikely that these two countries would be keen to join up with the Soviet Union, whose communist system the western democracies hated more that Hitler's fascist dictatorship.
Benito Mussolini suggested to Hitler that one way of solving this issue was to hold a four-power conference of Germany, Britain, France and Italy. This would exclude both Czechoslovakia and the Soviet Union, and therefore increasing the possibility of reaching an agreement and undermine the solidarity that was developing against Germany.
The meeting took place in Munich on 29th September, 1938. Desperate to avoid war, and anxious to avoid an alliance with Joseph Stalin and the Soviet Union, Neville Chamberlain and Edouard Daladier agreed that Germany could have the Sudetenland. In return, Hitler promised not to make any further territorial demands in Europe.

"Why are there so many troops?"
"In case of a provocation."
"What if there's no provocation?"
"How could there not be with so many troops?!"
On 29th September, 1938, Adolf Hitler, Neville Chamberlain, Edouard Daladier and Benito Mussolini signed the Munich Agreement which transferred the Sudetenland to Germany.
When Eduard Benes, Czechoslovakia's head of state, protested at this decision, Neville Chamberlain told him that Britain would be unwilling to go to war over the issue of the Sudetenland.
The German Army marched into the Sudetenland on 1st October, 1938. As this area contained nearly all Czechoslovakia's mountain fortifications, she was no longer able to defend herself against further aggression.
Primary Sources
(1) Neville Chamberlain, letter to King George VI (13th September, 1938)
The continued state of tension in Europe which has caused such grave concern throughout the world has in no way been relieved, and in some ways been aggravated by the speech delivered at Nuremberg last night by Herr Hitler. Your Majesty's Ministers are examining the position in the light of his speech, and with the firm desire to ensure, if this is at all possible, that peace may be restored.
On the one hand, reports are daily received in great numbers, not only from official sources but from all manner of individuals who claim to have special and unchangeable sources of information. Many of these (and of such authority as to make it impossible to dismiss them as unworthy of attention) declare positively that Herr Hitler has made up his mind to attack Czechoslovakia and then to proceed further East. He is convinced that the operation can be effected so rapidly that it will be all over before France or Great Britain could move.
On the other hand, Your Majesty's representative in Berlin has steadily maintained that Herr Hitler has not yet made up his mind to violence. He means to have a solution soon - this month - and if that solution, which must be satisfactory to himself, can be obtained peacefully, well and good. If not, he is ready to march.
In these circumstances I have been considering the possibility of a sudden and dramatic step which might change the whole situation. The plan is that I should inform Herr Hitler that I propose at once to go over to Germany to see him. If he assents, and it would be difficult for him to refuse, I should hope to persuade him that he had an unequalled opportunity of raising his own prestige and fulfilling what he has so often declared to be his aim, namely the establishment of an Anglo-German understanding, preceded by a settlement of the Czechoslovakian question.
Of course I should not be able to guarantee that Dr. Benes would accept this solution, but I should undertake to put all possible pressure on him to do so. The Government of France have already said that they would accept any plan approved by Your Majesty's Government or by Lord Runciman.
(2) Neville Chamberlain, radio broadcast (27th September, 1938)
How horrible, fantastic, incredible, it is that we should be digging trenches and trying on gas-masks here because of a quarrel in a far-away country between people of whom we know nothing! I would not hesitate to pay even a third visit to Germany, if I thought it would do any good.
Armed conflict between nations is a nightmare to me; but if I were convinced that any nation had made up its mind to dominate the world by fear of its force, I should feel that it must be resisted. Under such a domination, life for people who believe in liberty would not be worth living; but war is a fearful thing, and we must be very clear, before we embark on it, that it is really the great issues that are stake.
(3) Statement issued by Neville Chamberlain and Adolf Hitler after the signing of the Munich Agreement (30th September)
We, the German Führer and Chancellor and the British Prime Minister, have had a further meeting today and are agreed in recognizing that the question of Anglo-German relations is of the first importance for the two countries and for Europe.
We regard the agreement signed last night and the Anglo-German Naval Agreement as Symbolic of the desire of our two peoples never to go to war with one another again. We are resolved that the method of consultation shall be the method adopted to deal with any other questions that may concern our two countries.
(4) Winston Churchill, The Second World War (1948)
For the French Government to leave her faithful ally Czechoslovakia to her fate was a melancholy lapse from which flowed terrible consequences. Not only wise and fair policy, but chivalry, honour, and sympathy for a small threatened people made an overwhelming concentration. Great Britain, who would certainly have fought if bound by treaty obligations, was nevertheless now deeply involved, and it must be recorded with regret that the British Government not only acquiesced but encouraged the French Government in a fatal course.
(5) The Manchester Guardian (17th March, 1939)
Prague, a sorrowing Prague, yesterday had its first day of German rule - a day in which the Czechs learned of the details of their subjection to Germany, and in which the Germans began their measures against the Jews and against those people who have "opened their mouths too wide." Prague's streets were jammed with silent pedestrians wandering about, looking out of the corners of their eyes at German soldiers carrying guns, at armoured cars, and at other military precautions. Some Czechs were seen turning up their noses at the Germans. Germans were everywhere. Bridges were occupied by troops and each bridge-head had a heavy machine-gun mounted on a tripod and pointing to the sky. Every twenty yards along the pavement two machine-guns were mounted facing each other.
Suicides have begun. The fears of the Jews grow. The funds of the Jewish community have been seized, stopping Jewish relief work. The Prague Bar Council has ordered all its "non-Aryan" members to stop practicing at once. The organization for Jewish emigration has been closed. Hundreds of people stood outside the British Consulate shouting: "We want to get away!" This is only the beginning. According to an official spokesman of the German Foreign Office in Berlin last night, the Gestapo (secret police) will have rounded up hundreds of "harmful characters" within the next few days. So far about fifty to a hundred men have been put in local gaols. "There are certain centres of resistance which need to be cleaned up," said the spokesman. "Also some people open their mouths too wide. Some of them neglected to get out in time. They may total several thousand before we are through. Remember that Prague was a breeding-place for opposition to National Socialism." The head of the Gestapo in Prague is reported to have been more definite: "We have 10,000 arrests to carry out." Already, say Reuter's correspondent, everyone seems to have an acquaintance who has disappeared.